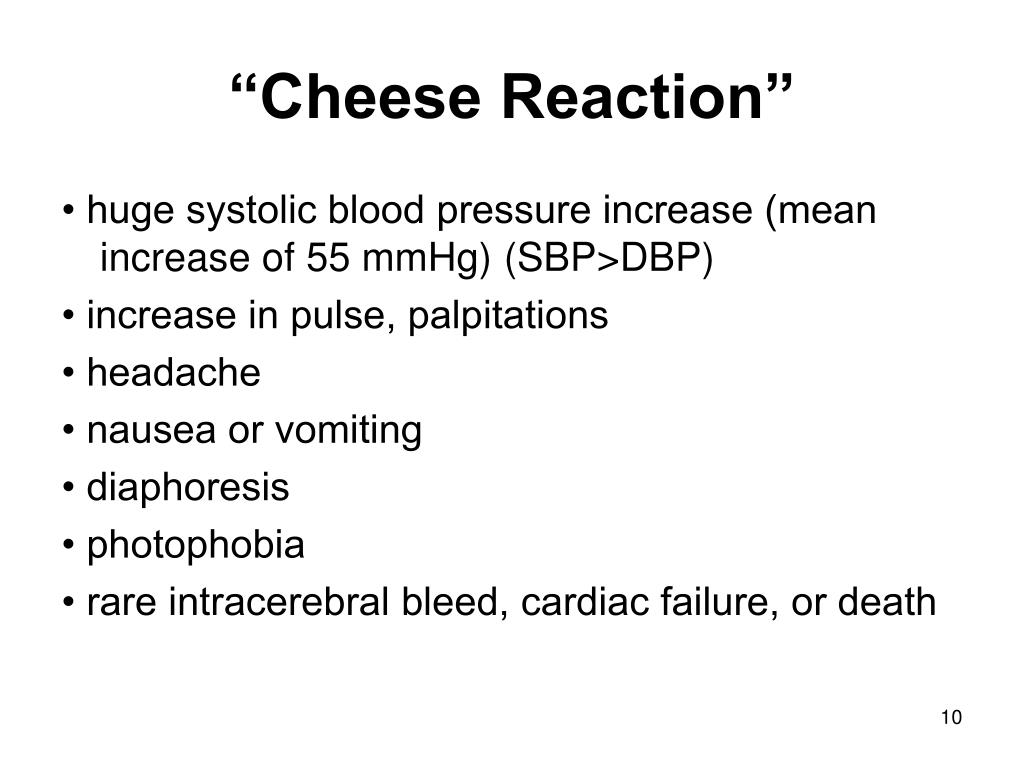
The tyramine reaction consists of a thumping heartbeat and a progressive increase in BP majority of them occurred before the cheese reaction was recognized (21 deaths inWhat is the Tyramine ("cheese") reaction?La cheese reaction è una sindrome causata dall'eccessivo accumulo di monoammine dovuto all'effetto della tiramina potenziato dall'utilizzo di farmaci antidepressivi contenenti inibitori delle monoamminossidasi (IMAO)

Tyramine And Norepinephrine Page 1 Line 17qq Com
What is the cheese effect with tyramine
What is the cheese effect with tyramine- · Transport studies with everted rat intestinal preparations indicate that tyramine is extensively metabolized during transport through the intestine Selective inhibition of MAOA by clorgyline results in a large increase in the amount of unchanged tyramine transported, whereas selective inhibition of MAOB with Ldeprenyl (selegiline) has no significant effectFirst described in a Bristish pharmacist's wife a very long time ago poor woman, every time she ate cheese she developed a severe headache Gradually discovered to be an interaction between monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs) and tyraminecontaining foods
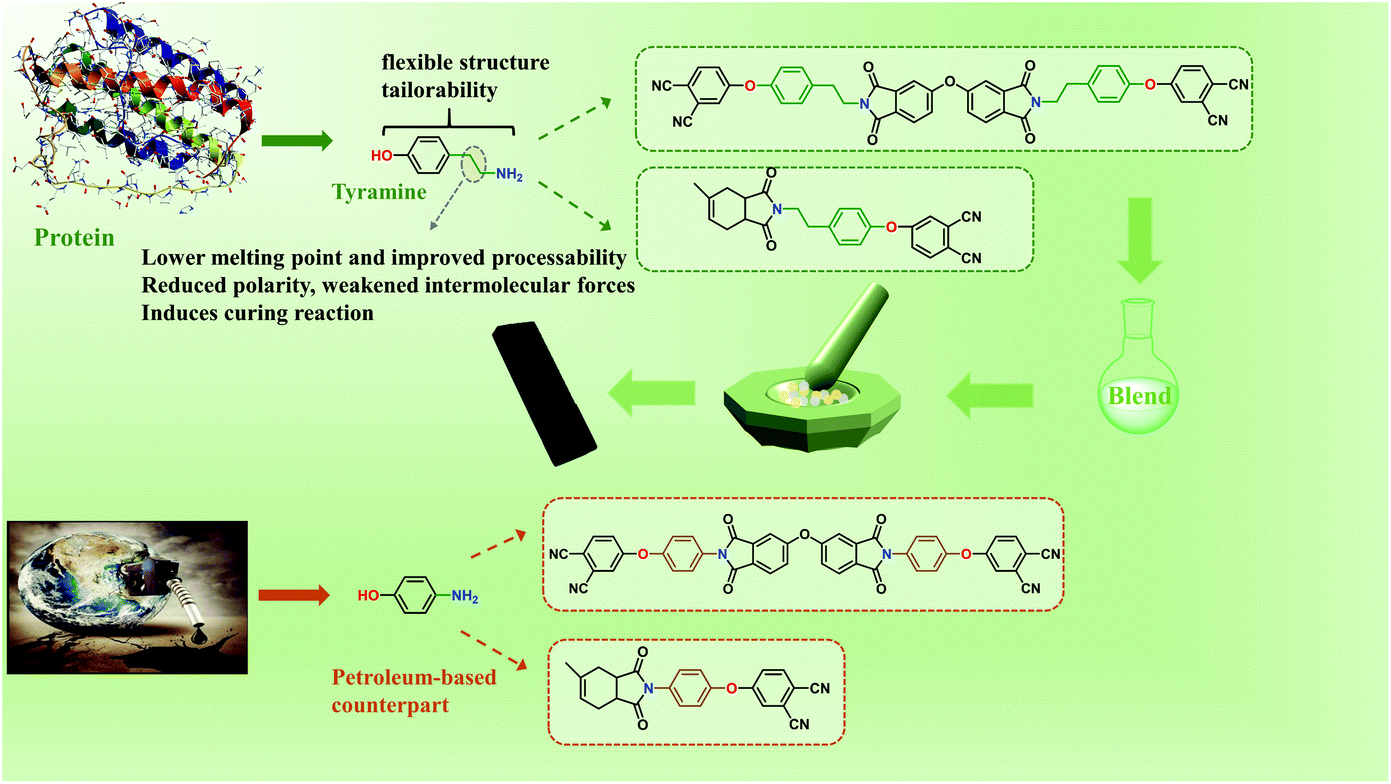


A New Molecular Design Platform For High Performance Polymers From Versatile Bio Based Tyramine A Case Study Of Tyramine Derived Phthalonitrile Resin Polymer Chemistry Rsc Publishing
Tyraminewise ie 100 grams of cheese in a meal is an unhealthily large portion A healthy portion is 25 grams Few cheeses (even 'mature' cheeses) contain more than 25 mg of tyramine in 100 grams (25 mg in 100 g = 250 mg/kg) So a 25 gram portion contains only 6 mg of tyramine and that is unlikely to cause a significant bloodMonoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs) are a class of drugs that inhibit the activity of one or both monoamine oxidase enzymes monoamine oxidase A (MAOA) and monoamine oxidase B (MAOB) They are best known as highly efficacious antidepressants, as well as effective therapeutic agents for panic disorder and social phobiaThey are particularly effective in treatmentresistantTyramine poisoning associated with cheese consumption is known as the 'cheese reaction,' with symptoms such as headache and hypertensive crisis From Encyclopedia of Food and Health , 16 Related terms
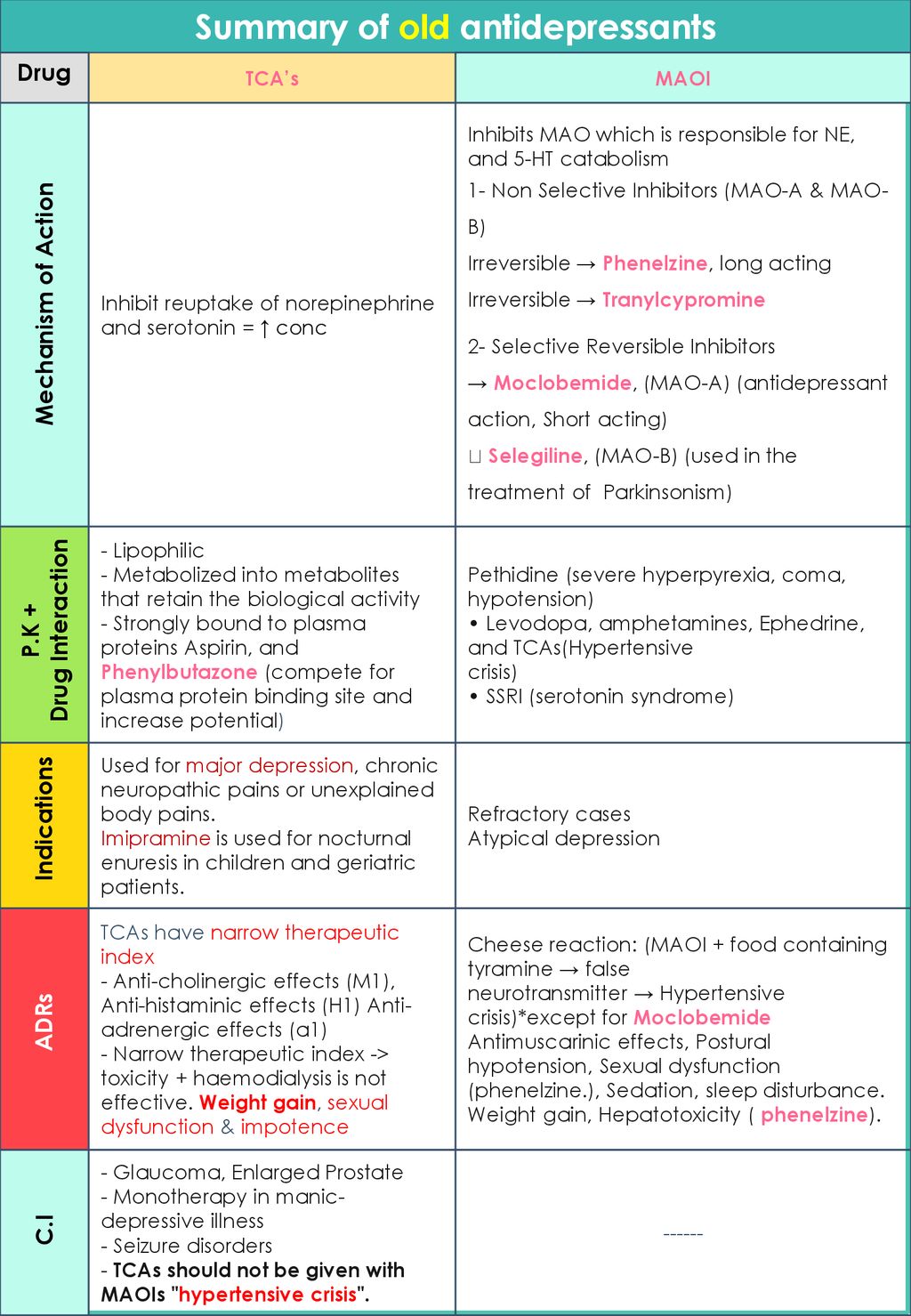
Cheese* / analysis Fluorometry Humans HydrogenIon Concentration Hypertension / chemically induced Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors / antagonists & inhibitors Mouth Mucosa / metabolism Tyramine / analysis Tyramine / metabolism*Response to tyramine ('cheese reaction'), is serotonin toxicity (ST) — aka serotonin syndrome That is now well defined and is straightforward to avoid by not coadministering any drug with serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SRI) potency There are no therapeutically used drugs, other than drugs with SRI activity, that are capable ofThe most feared interaction of MAOIs is the interaction with tyramine, a compound contained in a number of foods and beverages This interaction may lead to hypertensive crises the socalled 'cheese reaction'
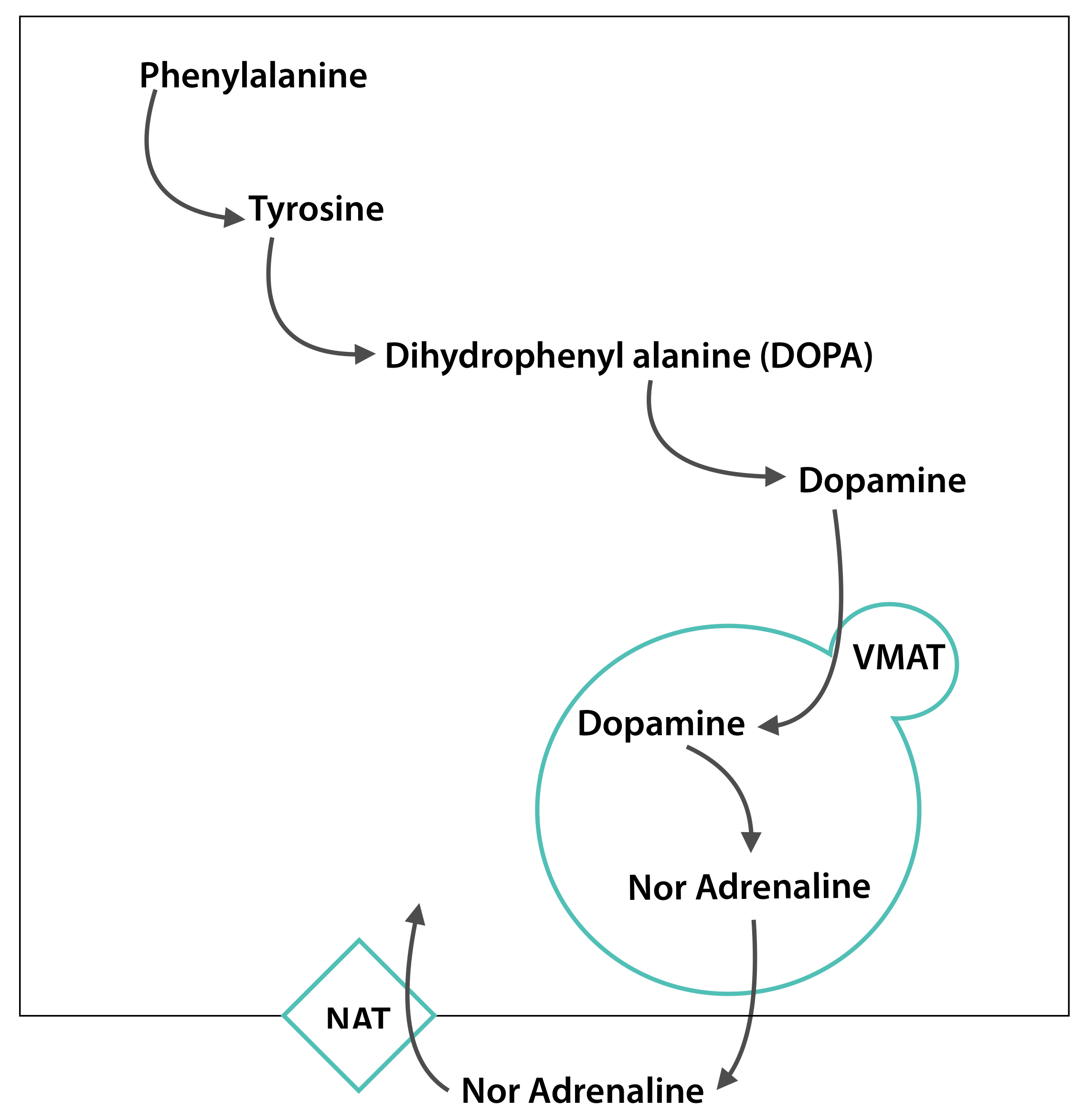
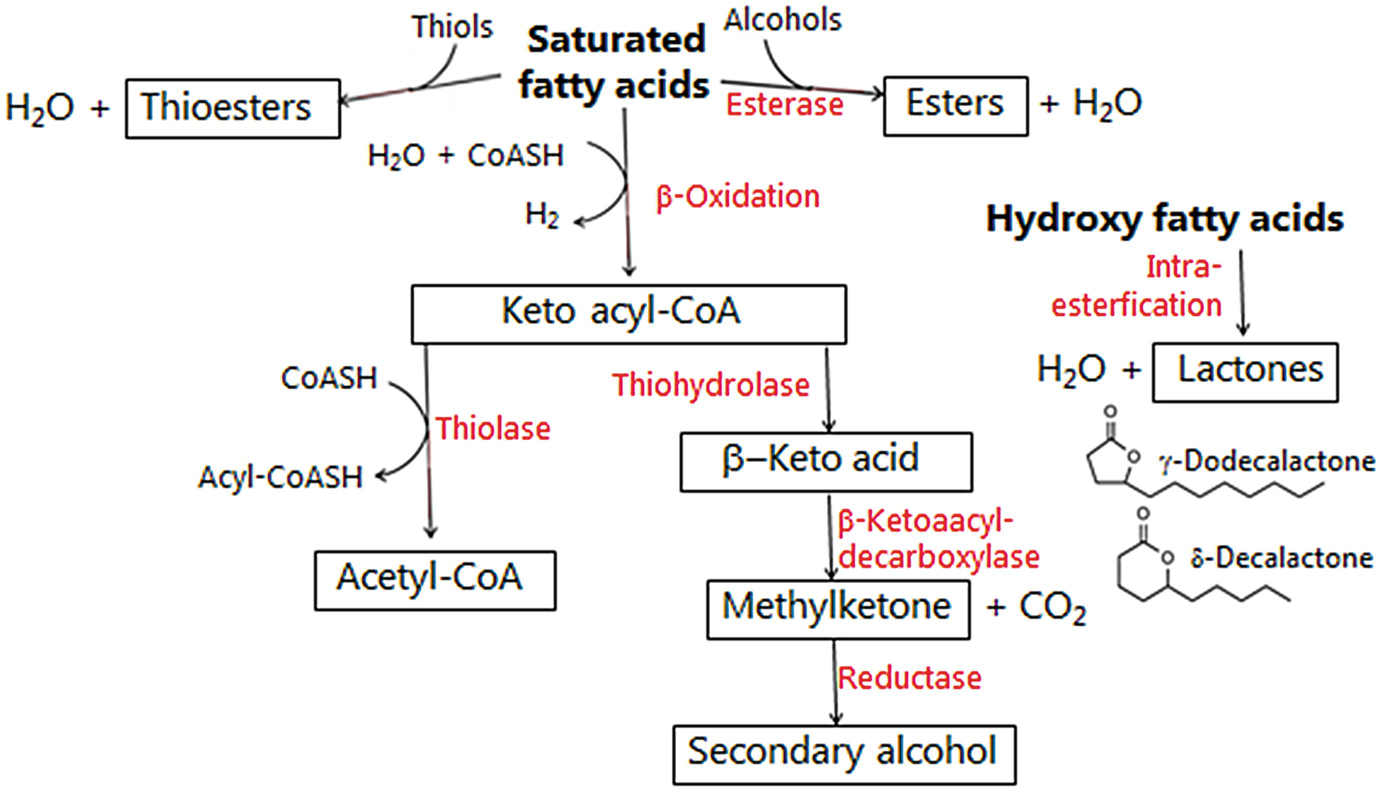
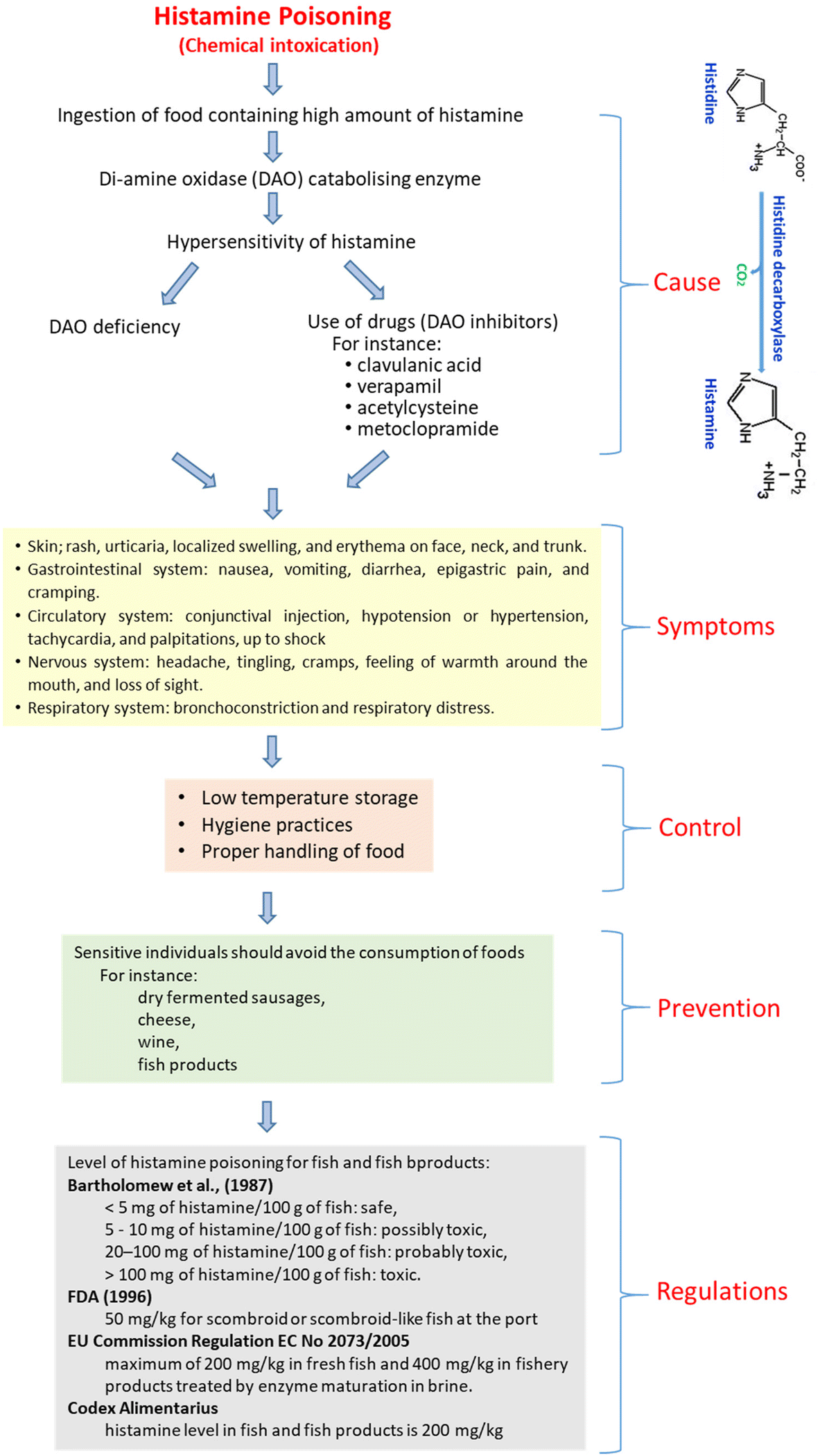
Tyramine is a vasoactive amine which promotes hypertension Causes the release of noradrenaline leading to elevated blood pressure; · The mechanism of potentiation of cardiovascular effects of tyramine, the cheese reaction, and NE release and metabolism after MAOA inhibition The demonstration that MAO was not a single enzyme but existed in several forms was strengthened by the observation that the MAO inhibitor clorgyline could differentiate between two forms of MAO1,2⇓ Johnson2 termed theseTyramine is metabolized by the enzyme monoamine oxidase In foods, it is often produced by the decarboxylation of tyrosine during fermentation or decay Foods containing considerable amounts of tyramine include fish, chocolate, alcoholic beverages, cheese, soy sauce, sauerkraut, and processed meat



Antipsychotics Antimanics Antidepressants Ppt Download
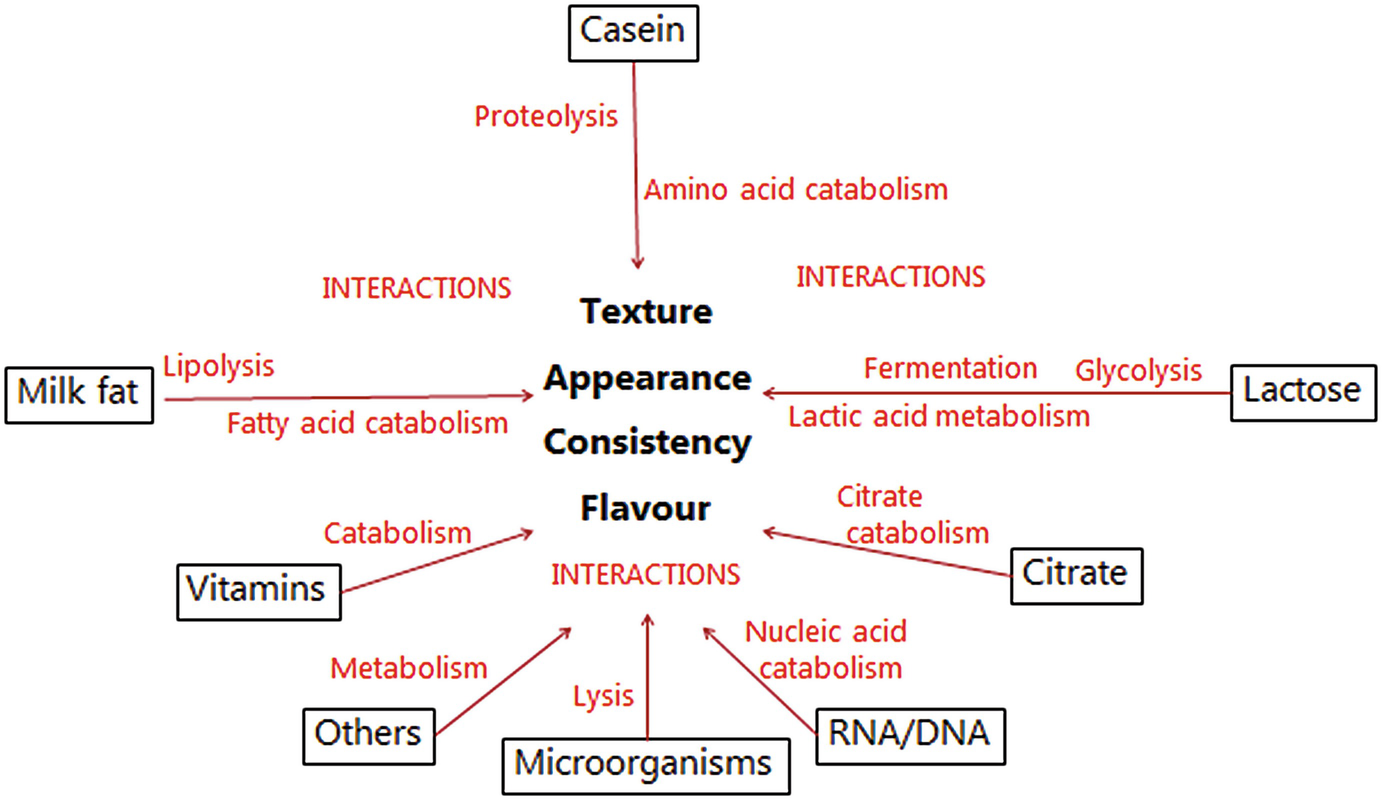


Enzymes In Cheese Ripening Springerlink
· Tyramine, 4 (2aminoethyl)phenol, the biogenic amine derivative of tyrosine is an active pressor amine, which occurs naturally in many foods and especially in fermented food products Tyramine is formed from decarboxilation of milk amino acids by metabolic activity of microorganisms during the cheese producing processesA rise in blood pressure (tyramine reaction)1 Foods and beverages your patients should avoid while taking ZEPOSIA Foods and beverages that are aged, fermented, cured, smoked, or pickled (eg, aged cheese, pickled herring) may be high in tyramine and should be avoided It's recommended that patients taking ZEPOSIA avoid foodsAnd Camembert Cheeses made from pasteurized milk are less likely to contain high levels of tyramine — for example, American cheese, cottage cheese, ricotta, farmer cheese and cream cheese



Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors Maoi Mechanism Of Action Psychopharmacology



Common Motifs Of Biogenic Amine And Polyamine Metabolism In Mammals Download Scientific Diagram
· Tyramine reaction This occurs after an ingestion of tyramine containing foods such as cheese and beer It precipitates am hypertensive crisis Patients may complain of headache, sweating, agitation and chest pain Complications include an intracranial bleed, rhabdomyolysis, acute renal failure and DICTyramine and irreversible monoamine oxidase inhibitors in clinical practice Cooper AJ(1) Author information (1)St Thomas Psychiatric Hospital, Ontario, Canada The cheese reaction following use of the irreversible monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs) began to be reported in the UK with increasing frequency from about 1961Cheese Reaction July 26, April 10, 12 by Anand Bhumkar Hypertensive reaction resulting fromrelease of noradrenaline by tyramine and other sympathomimetic amine as a consequence of irreversible inhibition of MAOA



Tyramine To Norepinephrine Maoi Page 1 Line 17qq Com



What Is Cheese Reaction Mao I Non Selective In Pharmacology Youtube
Amount of tyramine containing foods eaten Foods that can cause a severe reaction Cheese hard, soft, mature, processed or cheese spreads Foods containing cheese eg pizzas, lasagne, pies, quiche Sour cream Meat or yeast extracts or meals containing these extracts, eg Bovril®, Oxo®, Marmite®, gravy granules, stock cubes, · (Tyramine levels increase in foods when they are held at room temperature) Also avoid gravies and sauces made with meat extracts, soy products, or cheese Aged (mature) cheeses, including Cheddar, Stilton, Swiss, camembert, blue, and gorgonzola varietiesBlue cheeses such as Stilton and Gorgonzola;
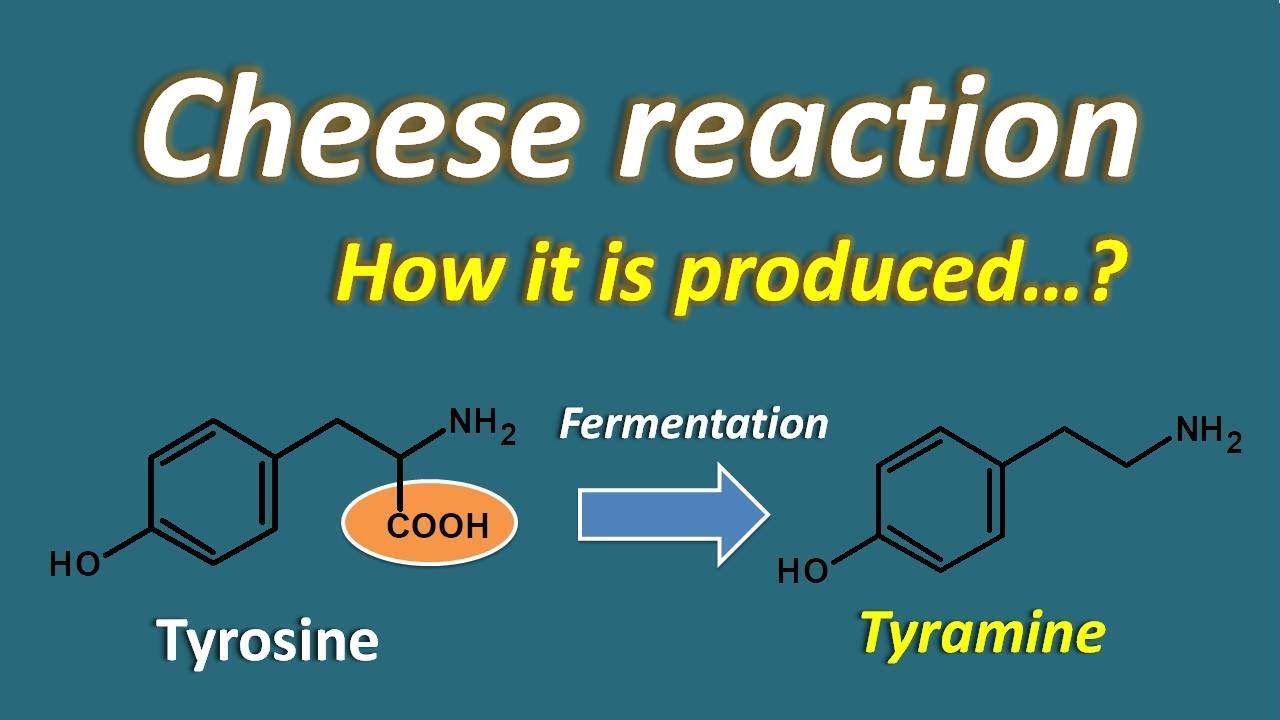


Cheese Reaction How It Is Produced Youtube



Maoi Toxicity Litfl Toxicology Library Toxicants
Maximum tolerable tyramine levels in cheese, fermented sausage, fish/fishery products, and sauerkraut could be 1000 mg kg −1, 00 mg kg −1, 950 mg kg −1, and 800 mg kg −1, respectively It was reported that normal consumption of tyramine is 100–800 mg kg −1 whereas levels higher than 1080 mg kg −1 are regarded as toxicCheese reaction is a food drug interaction shown by food containing tyramine when they are given with drugs like MAO inhibitors and linezolidTyramine is usually metabolised by monoamine oxidase (MOAA) In presence of monoamine oxidase inhibition, tyramine can accumulate
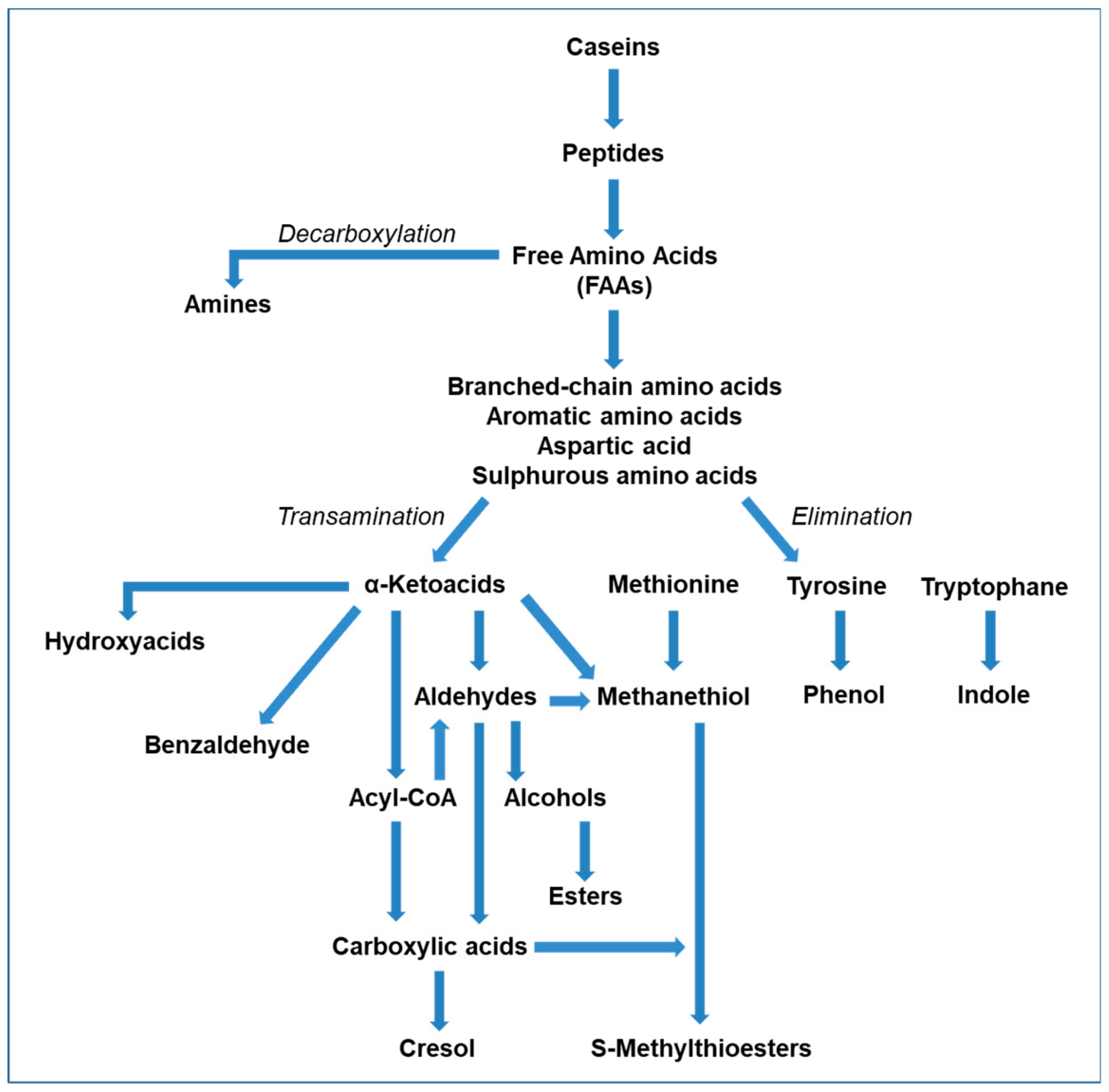


Molecules Free Full Text Volatile Flavor Compounds In Cheese As Affected By Ruminant Diet Html



Pdf Much Ado About Nothing Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors Drug Interactions And Dietary Tyramine
Examples of foods high in tyramine include Strong or aged cheeses, such as aged cheddar, Swiss and Parmesan; · Tyramine is a compound produced by the breakdown of an amino acid called tyrosine It's naturally present in some foods, plants, and animals Learn what tyramineTyramine is a monoamine and acts indirectly to release catecholamines Tyramine is typically metabolized by monoamine oxidase in the gut, a process that MAOIs interfere with Tyramine is found in preserved meat, fish, cheese, alcohol, and proteinrich foods which are particularly likely to contain bacteria that convert amino acids into monoamines like tyramine



Synthesis And Evaluation Of Nitrocatechol Derivatives Of Chalcone As Inhibitors Of Monoamine Oxidase And Catechol O Methyltransferase Semantic Scholar



Tyramine Or Cheese Reaction Hypertensive Crisis Moa Pharmacology Easy Explained Youtube
2602 · Tyramine Containing Foods are Often Cited as Migraine Triggers I f you've done some research on a Migraine diet, you've probably run across tyramine Tyramine is a byproduct found naturally in some foods—particularly those that are aged and fermented, like cheeseCheese made from pasteurized milk has lower levels of tyramine than aged cheeses American cheese, cottage cheese, ricotta, and cream cheese are safer alternatives 2Tyramine was estimated in 28 samples of 11 pieces of Gruyere cheese gruyere cheese Subject Category Commodities and Products see more details obtained from different sources Values were from 11 to 1184 µg per g Highest values were found close to the rind Cheese substance furthest removed from the rind contained only small amounts


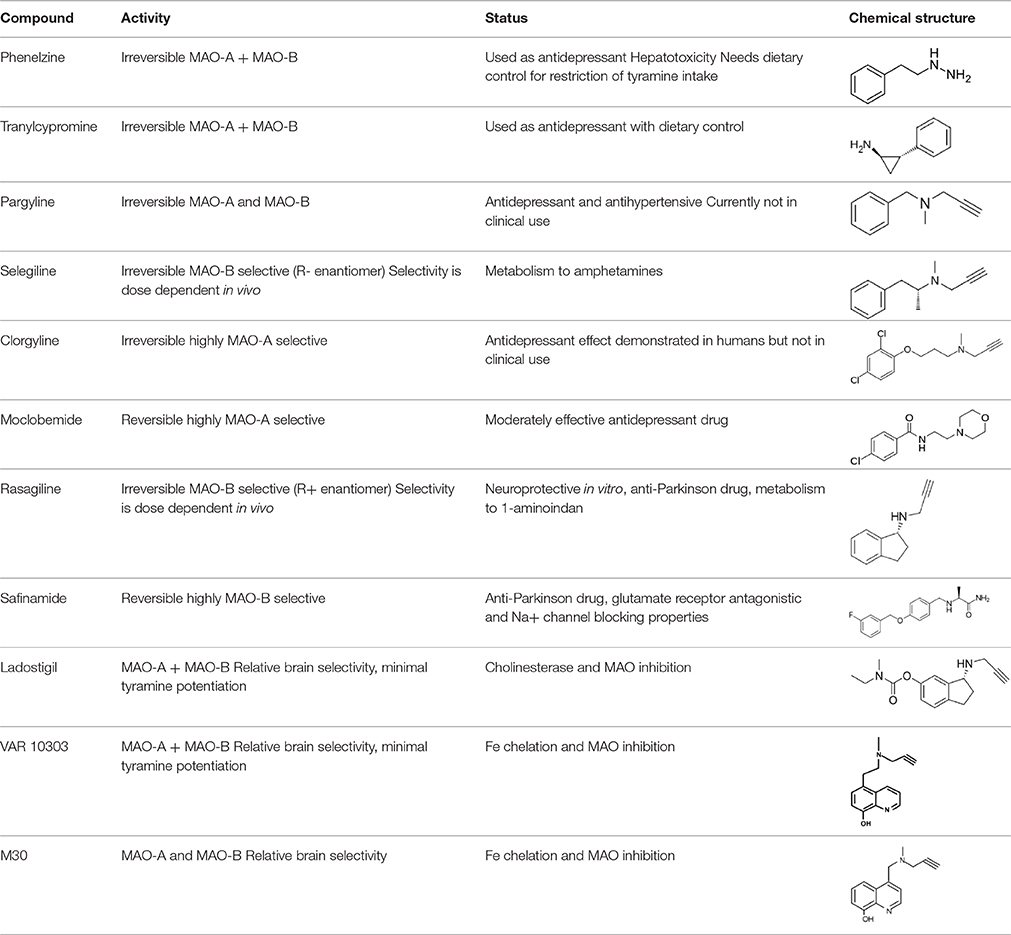
Selegiline Transdermal Wikidoc



Cheese Reaction Tyramine Sympathomimetics In Malayalam Youtube
Tyramine sensitivity can only be treated by diet I wonder if it ever goes away As furballsmom stated Gluten may be an issue I had to eliminate wheat too and no more peanut butter dang Bottom line is I eat like a cave man and so far so good Look up "cheese reaction" Comment0801 · An acute attack of hypertension that can occur in a person taking a monoamine oxidase inhibitor (MAOI) drug who eats cheese, caused by an interaction of the MAOI with tyramine, formed in ripe cheese when bacteria provide an enzyme that reacts with the amino acid tyrosine in the cheese Also called the cheese reaction · Some of the foods containing tyramine are aged cheese, nuts, herring, and chicken livers A more complete diet listing is available to members of the Foundation Foods with high concentration of tyramine are contraindicated with MAO1type antidepressants


Death By Chocolate The Cheese Reaction Firstclass



Taar1 Dependent And Independent Actions Of Tyramine In Interaction With Glutamate Underlie Central Effects Of Monoamine Oxidase Inhibition Biological Psychiatry
An indirect sympathomimetic that occurs naturally in cheese and other foods Tyramine does not directly activate adrenergic receptors, but it can serve as a substrate for adrenergic uptake systems and MONOAMINE OXIDASE to prolong the actions of adrenergic transmitters1802 · Under these conditions, the signal is measured after 30 min reaction (to obtain the highest sensitivity), but this time can be significantly reduced by increasing the temperature (the reaction is finished after 4 min when working at 50 °C) The method has been applied to tyramine determination in a cheese sample with good resultsAsatoor did extensive research and found that the combination of an MAOI and a food containing tyramine resulted in the hypertensive interaction ("the cheese reaction") Because of the risk of intracerebral hemorrhage and death, clinicians were hesitant to use the MAOIs



Molecular Abosortion Spectra Of Gold Nanoparticles Aunp Formation Download Scientific Diagram



Figure 5 From The Therapeutic Potential Of Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors Semantic Scholar
· An acute attack of hypertension that can occur in a person taking a monoamine oxidase inhibitor (MAOI) drug who eats cheese, caused by an interaction of the MAOI with tyramine, formed in ripe cheese when bacteria provide an enzyme that reacts with the amino acid tyrosine in the cheese Other foods and drinks that produce the same effect include04 · An acute attack of hypertension that can occur in a person taking a monoamine oxidase inhibitor (MAOI) drug who eats cheese, caused by an interaction of the MAOI with tyramine, formed in ripe cheese when bacteria provide an enzyme that reacts with the amino acid tyrosine in the cheese Also called the cheese reactionLearn the definition of 'tyramine cheese reaction' Check out the pronunciation, synonyms and grammar Browse the use examples 'tyramine cheese reaction' in the great English corpus



Ppt Tyramine Safety With Emsam Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id



Tyramine Headache Cure Page 1 Line 17qq Com
Tyramine was extracted with 5% perchloric acid from cheese, followed by cleanup on a C18cartridge Average recoveries of tyramine from cheeses spiked at'One piece with which Milne was pleased was his clarification of the tyramine monoamineoxidase inhibitor interaction (the 'cheese reaction')' 'These could lead to serious interactions with foods containing tyramine, alcohol, narcotics, and overthecounter decongestants'A cheese reaction to the antidepressant Nardil (phenelzine) is a serious health problem from an interaction between the drug and certain foods People who take Nardil have difficulty breaking down a substance in some foods called tyramine


Enzymes In Cheese Ripening Springerlink



Ppt Tyramine Safety With Emsam Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id
Tyramine rich foods sauerkraut, chicken liver, chocolate, and cheeses (Cheddar, Gruyère, and Stilton are especially high), alcohol/ wine, pickled fish (herring), broad beans, yeast extracts, tofu and soy sauce MECHANISM Tyramine is a byproduct of Tyrosine metabolism by MAO in the liverTypically it will have low bioavailability due to extensive firstpass effect in the liver · The presence of tyramineproducing bacteria was determined by PCR, and a good correlation obtained between the results of this method and tyramine detection by HPLC These methods could be used to complement one another in the detection and quantification of tyramine in cheese prevention of tyramine accumulation in cheese · The reaction to cheese described represents the "tyramine syndrome" or the so called "cheese reaction" Few such cases have been described previously in association with isoniazid treatment 1– 3 The syndrome is mainly characterised by skin flushing (facial, arms and upper body), tachycardia, dyspnoea, sweating, hypertension, conjuctival infection, and headache
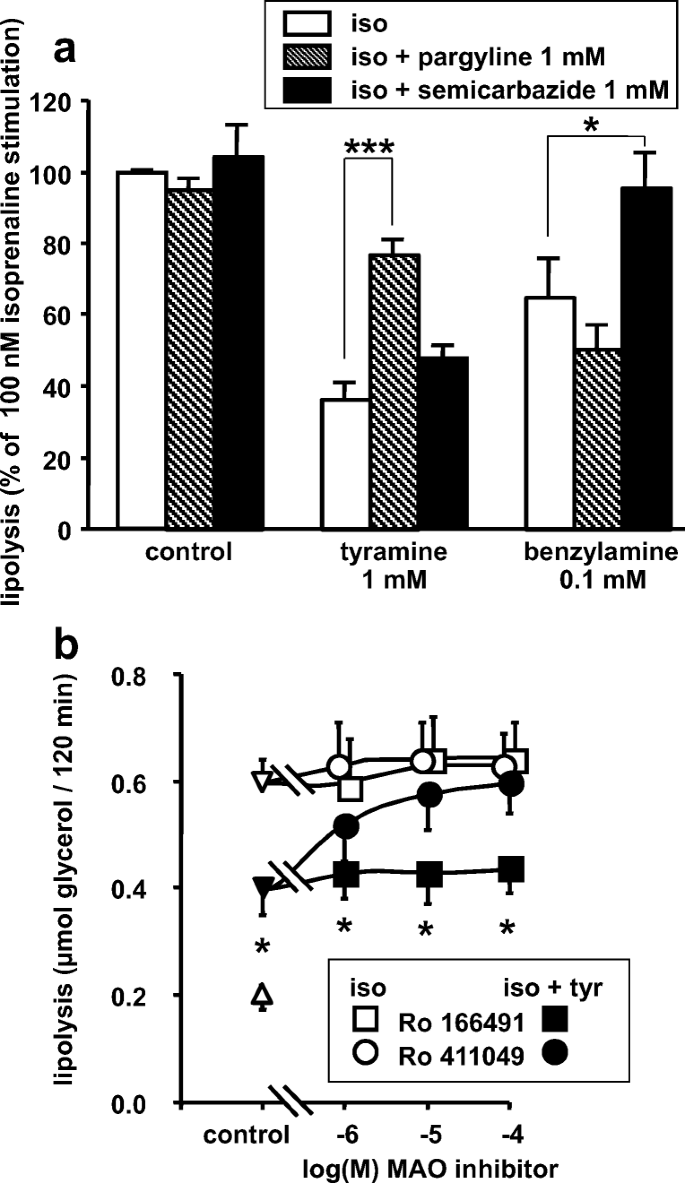


Mechanisms Of The Antilipolytic Response Of Human Adipocytes To Tyramine A Trace Amine Present In Food Springerlink



Cheese Reaction Pharmacology Tyramine Induced Hypertensive Crisis Youtube
Response to tyramine ('cheese reaction'), is serotonin toxicity (ST)— aka serotonin syndrome That is now well defined and is straightforward to avoid by not coadministering any drug with serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SRI) potency There are no therapeutically used drugs, other than drugs with SRI activity, that areAlthough tyramine is a substrate for both MAOA and B, it is only inhibitors of the former enzyme, which are also the effective antidepressants, that give rise to the cheese reaction This has be shown to be owing to MAOA being the major form of MAO in intestine and stomach Selective inhibition of that form of the enzyme results in substantialCheese reaction Acute hypertensive crisis associated with monoamine oxidase inhibitor (MAOI) drugs taken with cheese, caused by an interaction of the MAOI with tyramine, formed in ripe cheese when bacteria provide an enzyme that reacts with the amino acid tyrosine in the cheese



Cheese Reaction Tyramine Page 1 Line 17qq Com



Meal Ideas And Menus Avoiding High Tyramine Foods Made Easy Kathrynne Holden Ms Rd Pdf Free Download
Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitor (MAOI) related tyramine reaction MAOIs reduce first pass metabolism of tyramine, allowing greater concentrations to reach the sy



Pharmacotherapy Of Bipolar Disorder Ppt Video Online Download



How To Avoid Red Wine Headaches Fix Com


Ppt Tyramine Safety With Emsam Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id



Tyramine Tyrosine Metabolism Page 1 Line 17qq Com



Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors Osmosis



Leap Mrt Test The Nutrition Clinic For Digestive Health



Taar1 Dependent And Independent Actions Of Tyramine In Interaction With Glutamate Underlie Central Effects Of Monoamine Oxidase Inhibition Biological Psychiatry



A New Molecular Design Platform For High Performance Polymers From Versatile Bio Based Tyramine A Case Study Of Tyramine Derived Phthalonitrile Resin Polymer Chemistry Rsc Publishing



Pdf Biogenic Amines Residues In Canned Fish


Drugs Used In Depression Old New Ppt Download



Tyramine Produced By Enterococcal Strains In Phosphate Citrate Buffer Download Scientific Diagram


Chapter 1 Biogenic Amines Formation Toxicity Regulations In Food Rsc Publishing Doi 10 1039



Meal Ideas And Menus Avoiding High Tyramine Foods Made Easy Kathrynne Holden Ms Rd Pdf Free Download



Body Fat Reduction Without Cardiovascular Changes In Mice After Oral Treatment With The Mao Inhibitor Phenelzine Carpene 18 British Journal Of Pharmacology Wiley Online Library



Cheese Reaction Tyramine Page 1 Line 17qq Com



Dietary Restrictions Drug Interactions With Maoi Psychiatrist Com



Cheese Reaction Maoi Page 1 Line 17qq Com



Tyramine Reaction Page 2 Line 17qq Com


Frontiers Inhibitors Of Mao A And Mao B In Psychiatry And Neurology Pharmacology



Antidepressants Vaughan Asburys General Ophthalmology 17th Ed
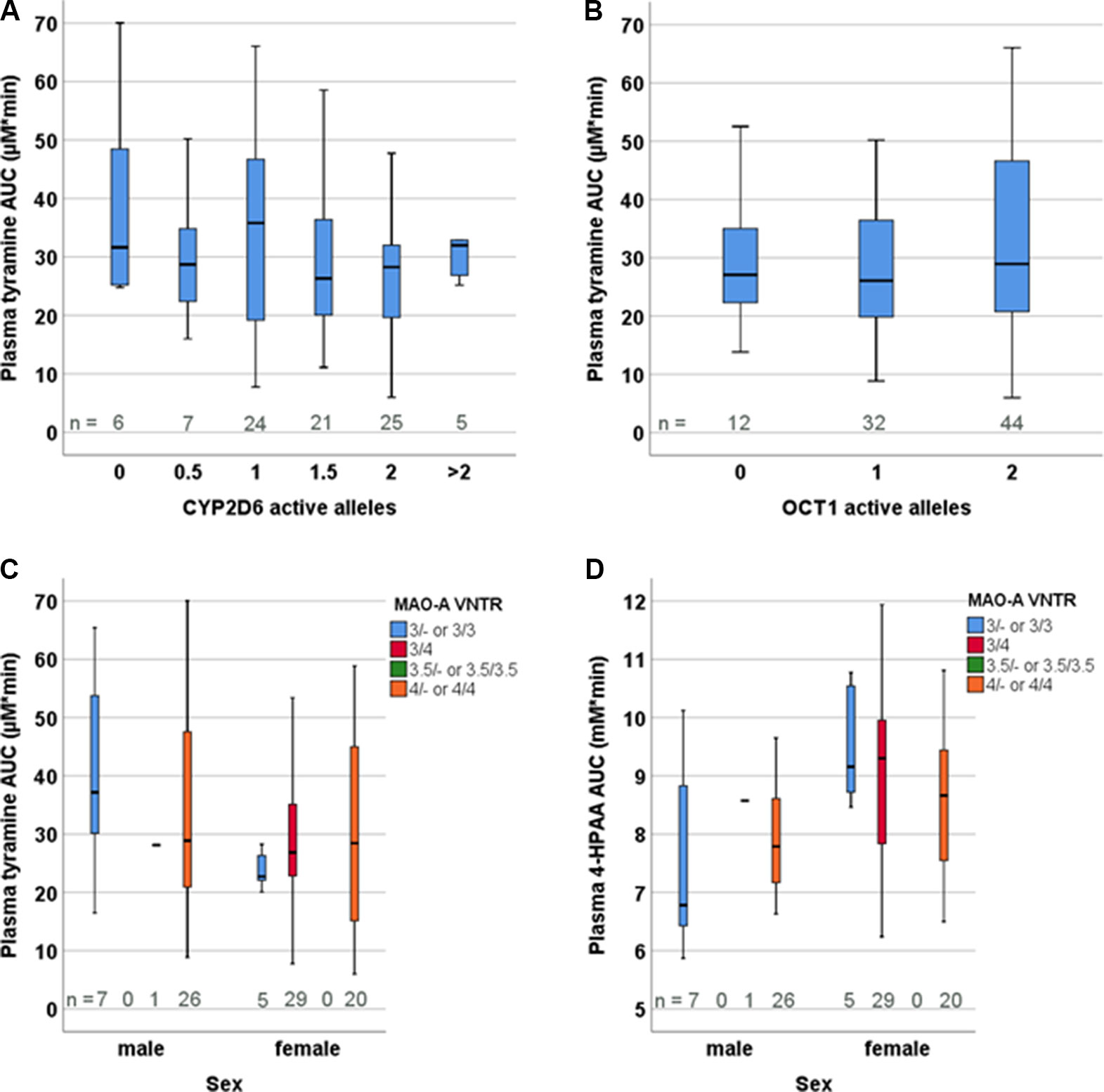


Frontiers Highly Variable Pharmacokinetics Of Tyramine In Humans And Polymorphisms In Oct1 Cyp2d6 And Mao A Pharmacology



A Review Of The Mechanisms And Role Of Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors In Parkinson S Disease Neurology


Pdf Hypertensive Crisis And Cheese
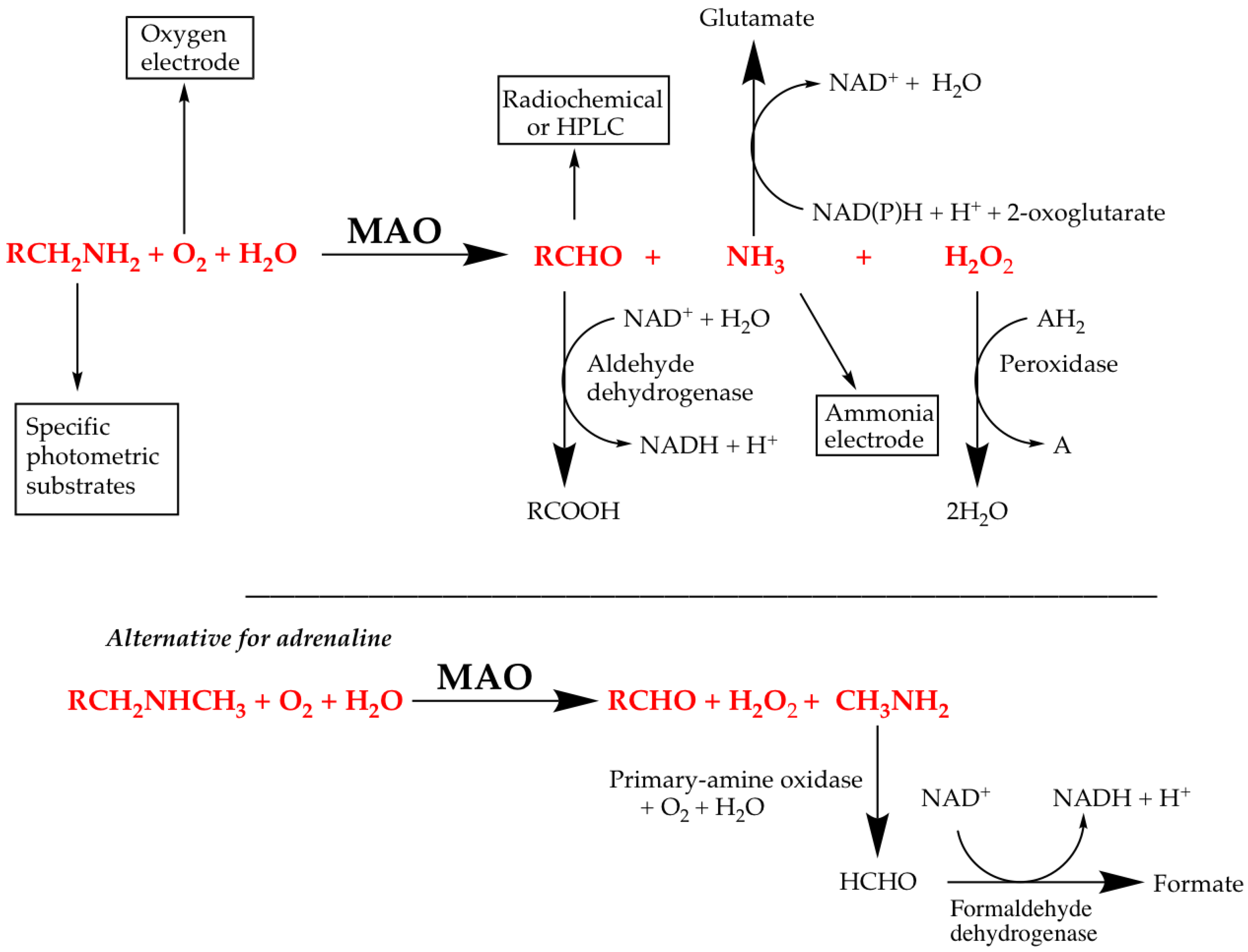


Molecules Free Full Text Assessment Of Enzyme Inhibition A Review With Examples From The Development Of Monoamine Oxidase And Cholinesterase Inhibitory Drugs Html


Cheese Reaction Mechanism Mao Inhibitors Tyramine Drug Interactions Pharmacology Made Easy Youtube


Pdf Tyramine In Malt Beverages Interfering With Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitor Drugs



Curcumin And The Mao Inhibitor Cheese Effect From Induced Info


Frontiers The Neural Bases Of Disgust For Cheese An Fmri Study Human Neuroscience


Maoi Toxicity Litfl Toxicology Library Toxicants



Taar1 Dependent And Independent Actions Of Tyramine In Interaction With Glutamate Underlie Central Effects Of Monoamine Oxidase Inhibition Biological Psychiatry



Psychostimulants Adaptogens Analeptics Antidepressants And Nootropic Drugs Online Presentation


Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors From Classic To New Clinical Approaches Springerlink
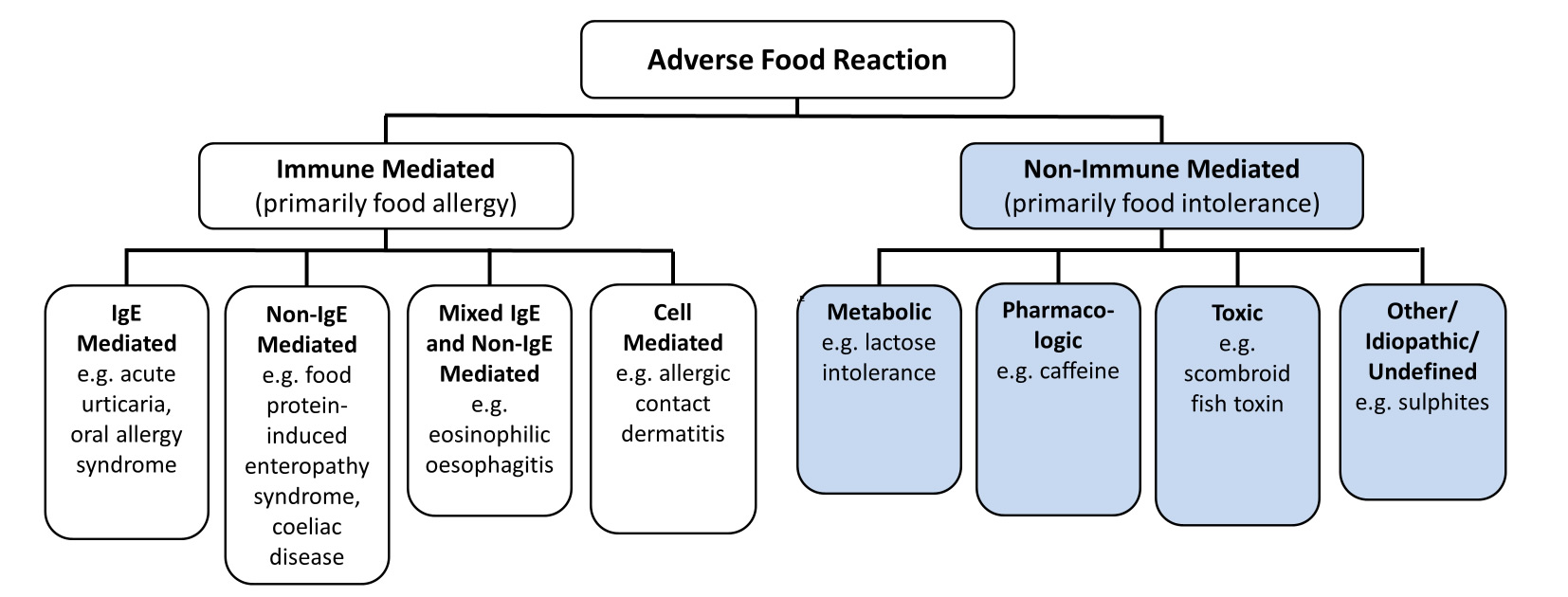


Food Intolerance Australasian Society Of Clinical Immunology And Allergy Ascia
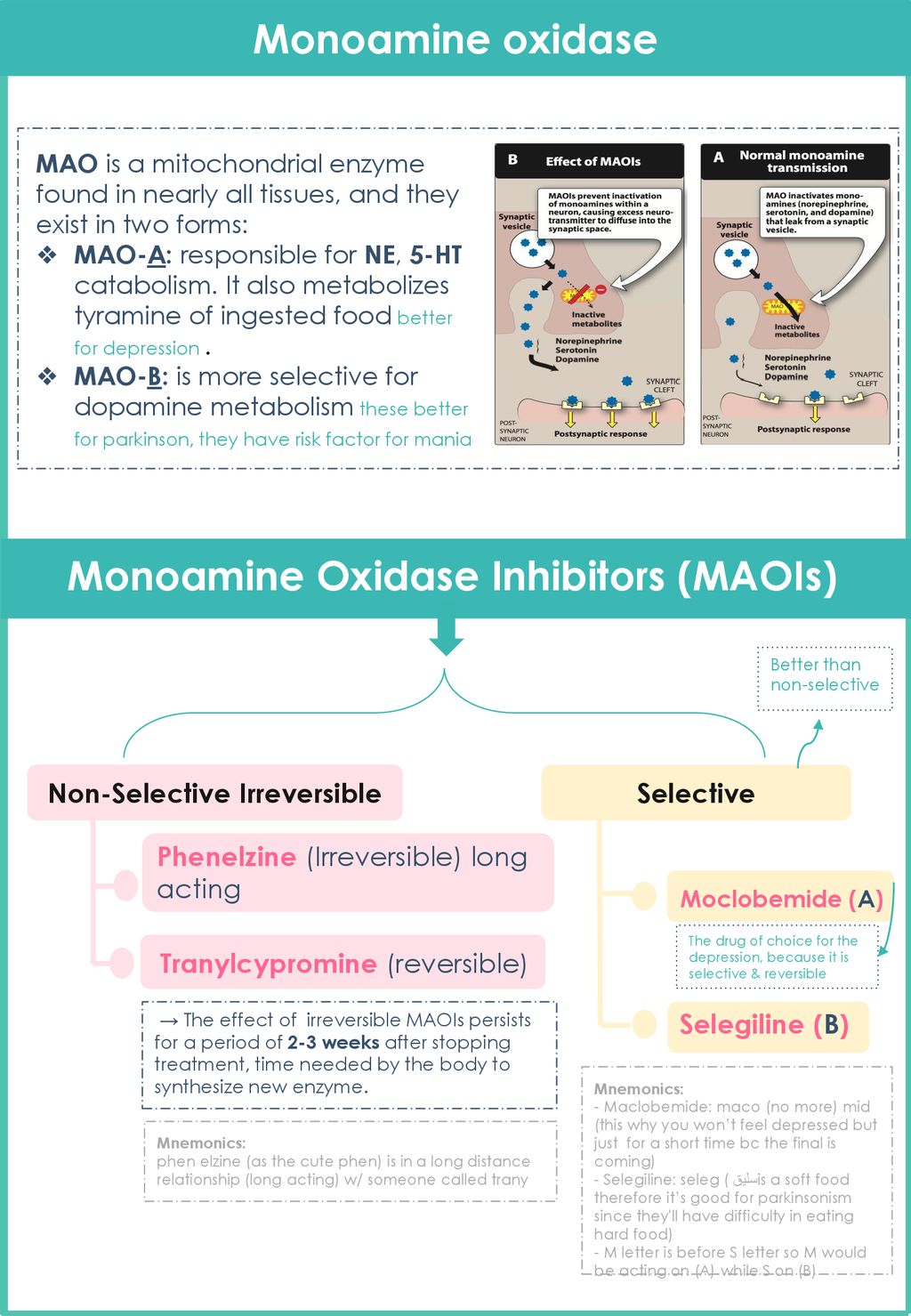


Drugs Used In Depression Old New Ppt Download



Drugs Used In Depression Old New Ppt Download



Body Fat Reduction Without Cardiovascular Changes In Mice After Oral Treatment With The Mao Inhibitor Phenelzine Carpene 18 British Journal Of Pharmacology Wiley Online Library



Cheese Reaction Pharmacology Youtube



A Clinical Overview Of Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors Pharmacological Profile Efficacy Safety Tolerability And Strategies For Successful Outcomes In The Management Of Major Depressive Disorders Psychiatric Annals



A Review Of The Mechanisms And Role Of Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors In Parkinson S Disease Neurology



Tyramine Tyrosine Metabolism Page 1 Line 17qq Com



Review Article The Diagnosis And Management Of Food Allergy And Food Intolerances Turnbull 15 Alimentary Pharmacology Amp Therapeutics Wiley Online Library


Edible Answers To Insomnia A Search For Nutritional Solutions For Sleepless Nights Kqed



Dietary Factors
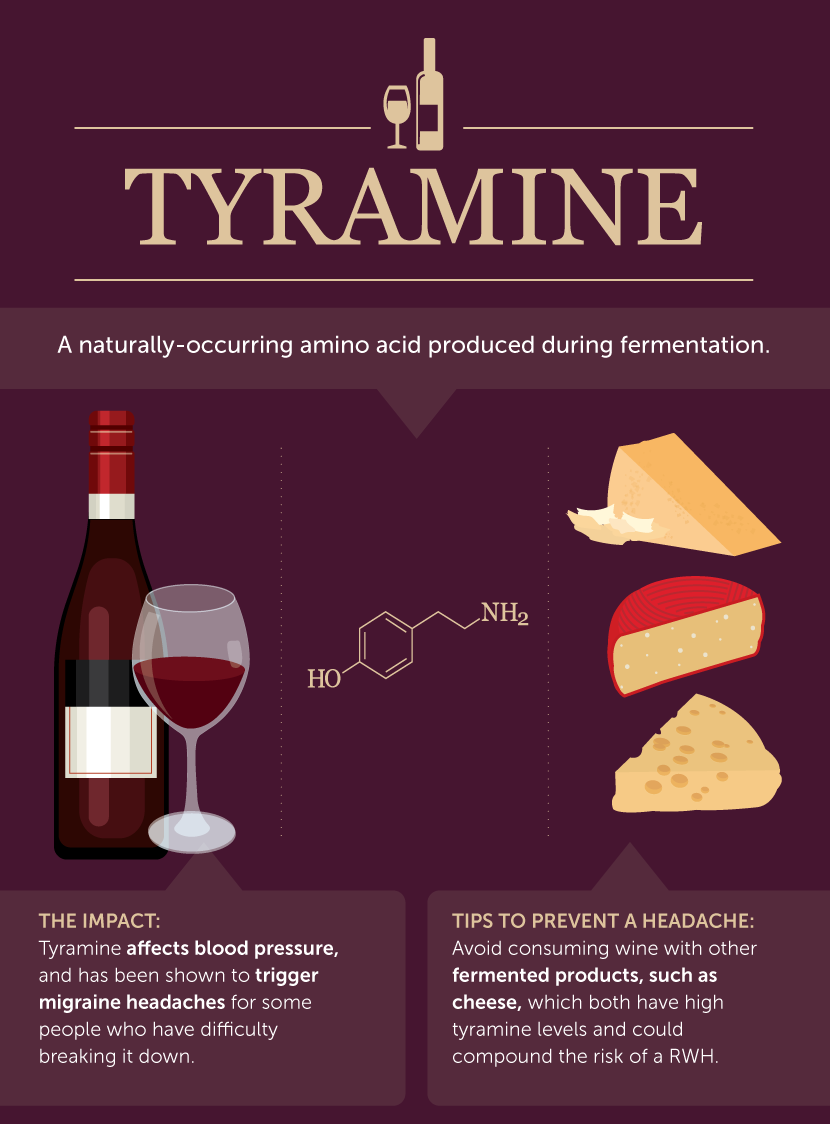


How To Avoid Red Wine Headaches Fix Com
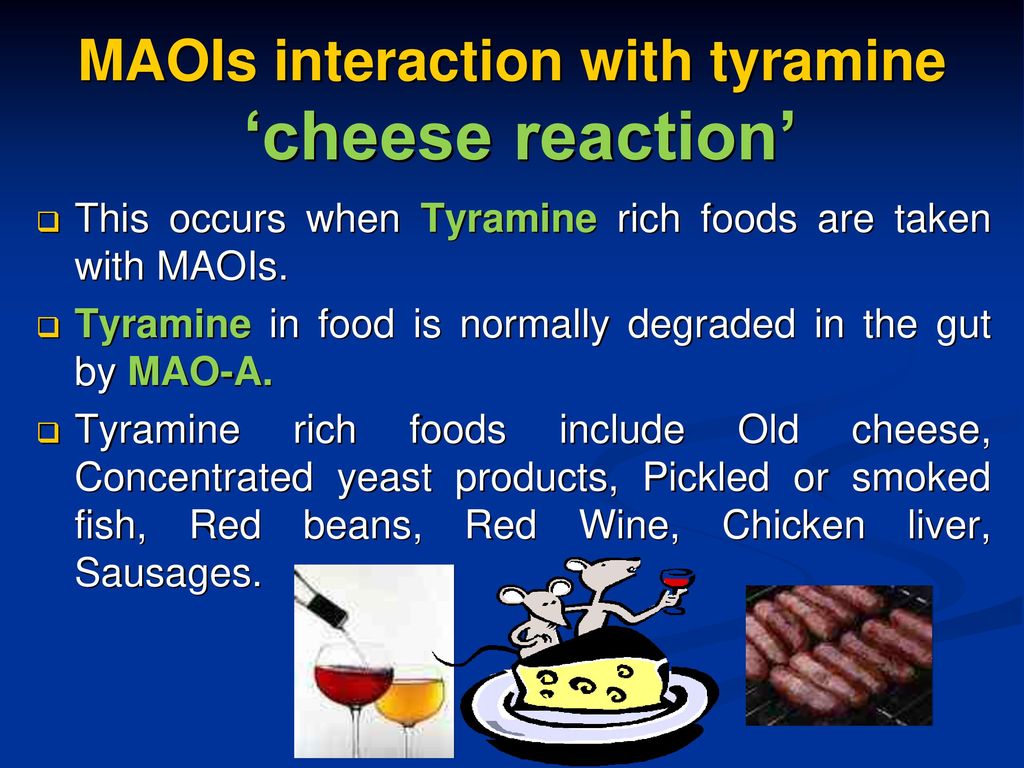


Drugs Used In Depression Prof Yieldez Bassiouni Ppt Download
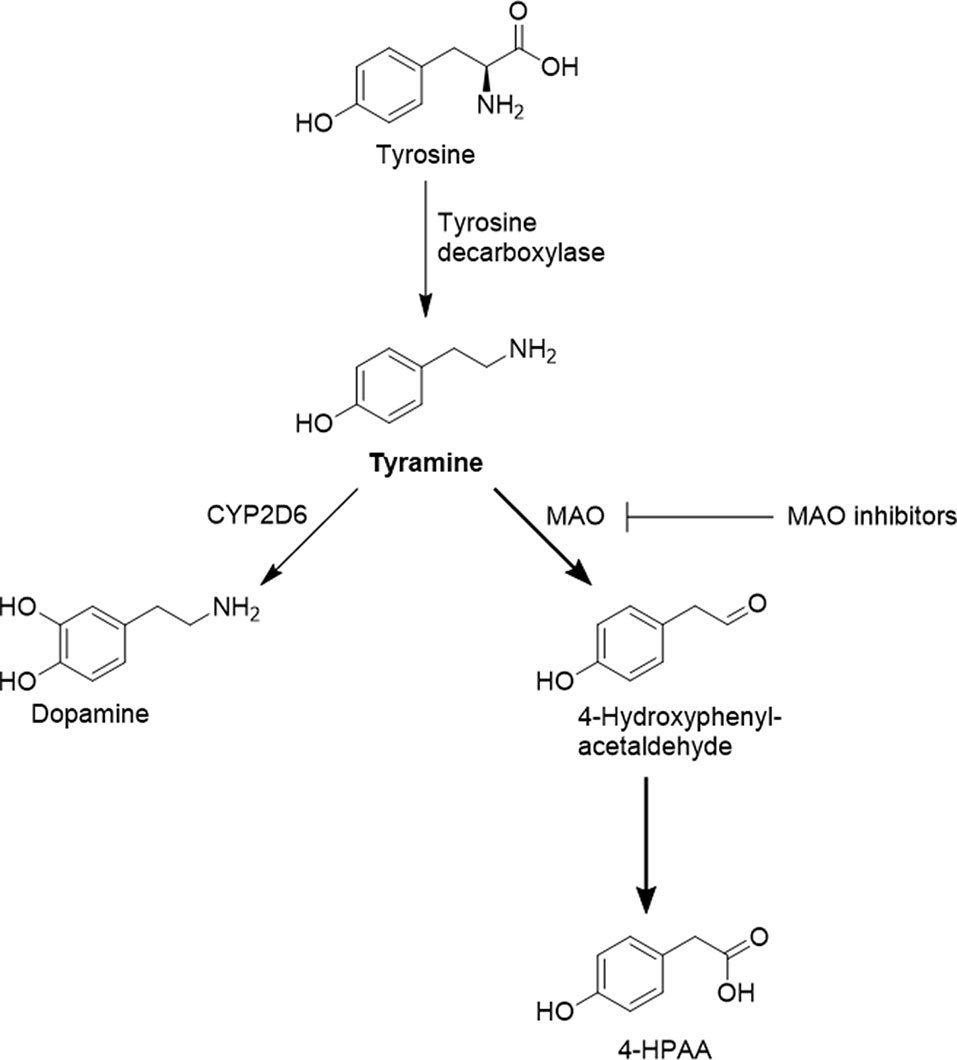


Frontiers Highly Variable Pharmacokinetics Of Tyramine In Humans And Polymorphisms In Oct1 Cyp2d6 And Mao A Pharmacology



Ppt Informed Consent Risk Of Cheese Reaction Powerpoint Presentation Id



Tyramine And Norepinephrine Page 1 Line 17qq Com



Body Fat Reduction Without Cardiovascular Changes In Mice After Oral Treatment With The Mao Inhibitor Phenelzine Carpene 18 British Journal Of Pharmacology Wiley Online Library



Antidepressants Drugs Which Can Elevate Mood Mood Elevators Ppt Download



Drugs Used In Depression Prof Yieldez Bassiouni Ppt Download



Tyramine Reaction Page 4 Line 17qq Com



Tyramine Food Examples Page 2 Line 17qq Com



Cheese Reactions Tyramine X Mao Inhibitors Pharmacology Easymedicinelearning Youtube
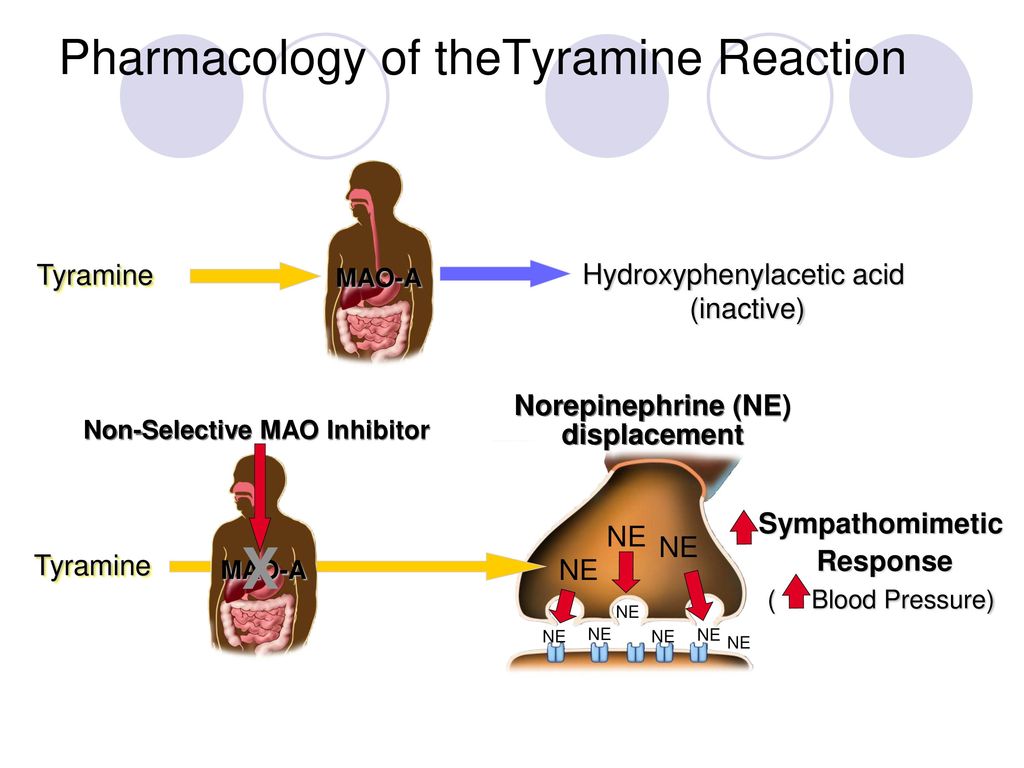


Antidepressants Drugs Which Can Elevate Mood Mood Elevators Ppt Download



Tyramine Wikipedia



Disposable Amperometric Biosensor Based On Poly L Lysine And Fe3o4 Nps Chitosan Composite For The Detection Of Tyramine In Cheese Dalkiran 19 Electroanalysis Wiley Online Library



Cheese Reaction Mechanism Mao Inhibitors Tyramine Drug Interactions Pharmacology Made Easy Youtube



Maoi Drugs News



Body Fat Reduction Without Cardiovascular Changes In Mice After Oral Treatment With The Mao Inhibitor Phenelzine Carpene 18 British Journal Of Pharmacology Wiley Online Library



Cheese Reactions Tyramine X Mao Inhibitors Pharmacology Easymedicinelearning Youtube


Beverages Free Full Text Biogenic Amines In Alcohol Free Beverages Html
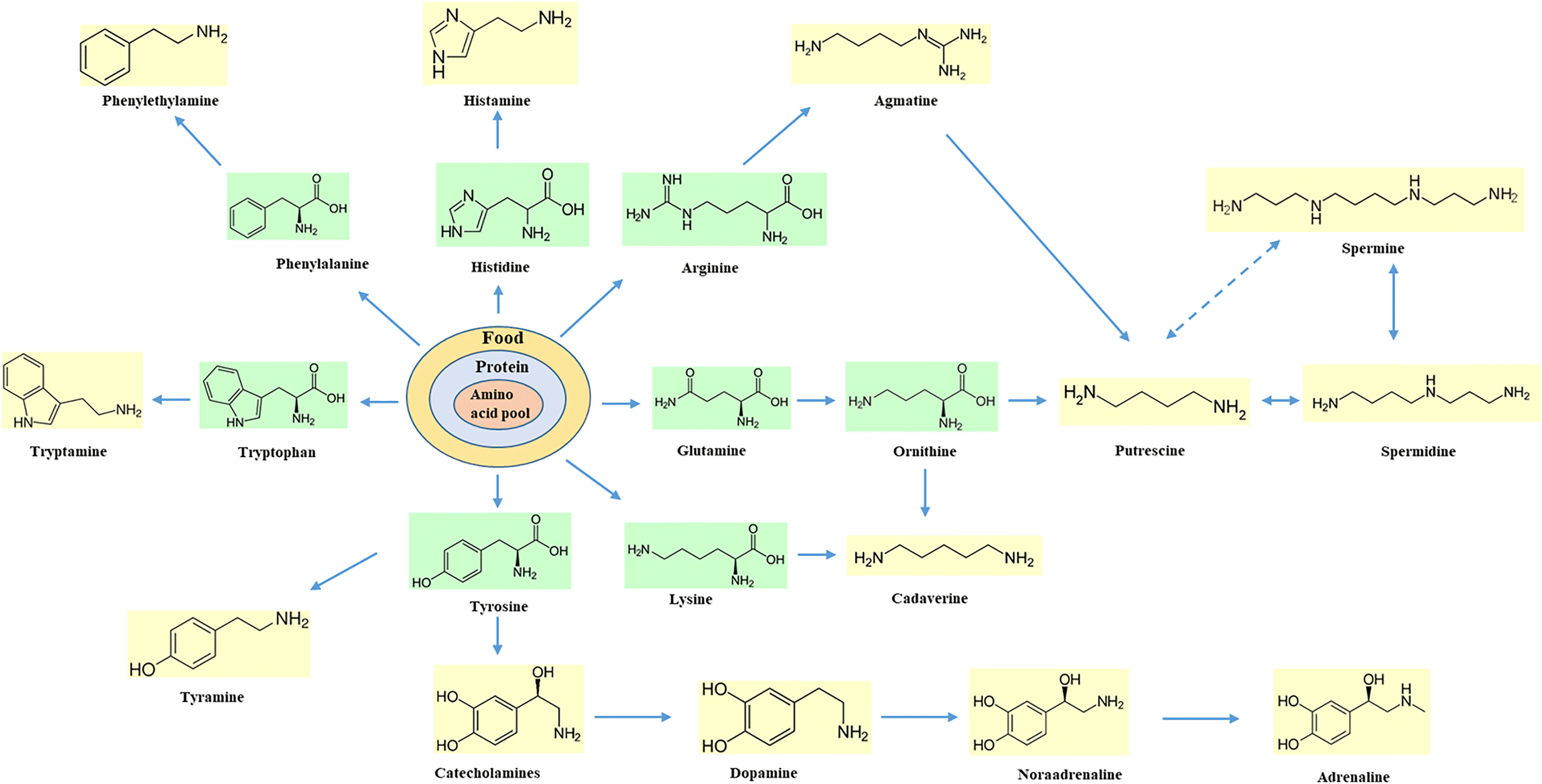


Chapter 1 Biogenic Amines Formation Toxicity Regulations In Food Rsc Publishing Doi 10 1039
/brewers-yeast-breastfeeding-and-breast-milk-supply-431836-FINAL-523435d7e1e847259e7dcb296b6603ff.png)


Brewer S Yeast Benefits Side Effects Dosage Interactions



Sembragiline A Novel Selective Monoamine Oxidase Type B Inhibitor For The Treatment Of Alzheimer S Disease Journal Of Pharmacology And Experimental Therapeutics



Tyramine Reaction Page 4 Line 17qq Com



Ppt Tyramine Safety With Emsam Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿